In this walkthrough, I will show how you can perform exploratory data analysis on stock market data using Azure Synapse serverless SQL pools. To simplify things I will just focus on daily quotes for the S&P 500.
The S&P 500 (short for Standard & Poor's 500) tracks the performance of 500 large companies listed on exchanges in the United States. The composition of the S&P 500 is typically rebalanced four times per year. The S&P 500 is a capitalization-weighted index meaning that the stocks with a higher market capitalization have a big impact on the changes in the index (See Top 10 S&P 500 stocks by index weight)

I downloaded all daily data for the S&P 500 stock market index (ticker symbol is ^GSPC) from Yahoo Finance using the historical data tab in CSV format. The S&P CSV file contains the date, open, high, low, close, volume, dividends and stock splits for the S&P 500 from December 1927 (but the index in its current form was only created in 1957) until now (dividends and stock splits are not relevant). I manually downloaded the file but take a look at Using Python and Pandas Datareader to retrieve financial data part 3: Yahoo Finance and Using the yFinance Python package to download financial data from Yahoo Finance for ways to automate retrieving data from Yahoo Finance using Python.
Serverless SQL Pools in Azure Synapse
Serverless SQL Pool is an auto-scale SQL query engine that is built-in to Azure Synapse - as the term serverless indicates you don't need to worry about provisioning underlying hardware or software resources. Serverless SQL Pool uses a pay-per-use model so you will only be charged for a query if you run it to process data. Like Synapse dedicated SQL pool, serverless SQL pool also distributes processing across multiple nodes using a scale-out architecture (Check out the
Microsoft research publication Polaris: the distributed SQL engine in Azure Synapse for an in-depth discussion).
Synapse Serverless SQL enables you to query external data stored in Azure Storage (including Data Lake Gen 1 and Data Lake Gen2), Cosmos DB and Dataverse. The data remains stored in Azure storage in a supported file format (CSV, JSON, Parquet or delta) and is query processing is handled by the Synapse SQL engine.
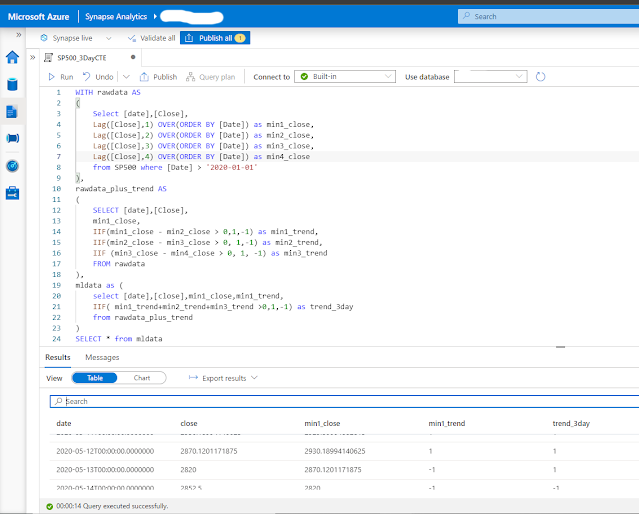
Walkthrough: analyzing S&P 500 data with Synapse serverless SQL
In this post I will not show you how you need to setup Azure Synapse - take a look at Quickstart: Create a Synapse Workspace for a detailed walkthrough - the Microsoft Learn learning paths which I added in the references are also quite useful.
In this post, I will be primarily using SQL to analyze the data but this is a matter of preference (having a coding background I prefer Python to do exploratory data analysis)
After you downloaded the data you will need to upload the CSV file to the Azure data lake storage associated with Synapse Link (you can also use a different Azure storage).
The OpenRowset (Bulk..) function allows you to access files in Azure storage. The SP500.csv file has a header row specifying the different columns in use - it contains all daily ticker data since December 1927. I am using Parser_Version 2.0 since it is more performant but it has some limitations (see the Arguments section in Microsoft's OpenRowSet documentation) - also check out How do Synapse serverless SQL pools deal with different file schemas (or schema evolution) part 1 CSV for some interesting info on how schema changes are handled.
If you will be using the data quite frequently, it might make more sense to use a CETAS process (CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE AS SELECT) to generate a dataset pointing to the data residing in the data lake ready for querying. In the Synapse Studio data hub, you can simply right click on a file and select the option to create an external table.
Next, select the database and the name of the table. You will need to create the external table by selecting "Use SQL Script" since you will need to adapt the script to skip the header row for reading data. For CSV files you have the option to infer column names.
You will need to modify the generated script for creating the external file format so that it skips the header row. You are still able to modify the database in which you want to create the external table (1) and I added a line to indicate that the external file contains a header row so data read should start on row 2 (2). Once you understand the script, it also possible to modify it to use wildcards, so that you can read from multiple files in multiple folders.
Now let's try out some queries in Azure Synapse Studio: